Throughout this research study, we break down most of the data between small homes, medium-sized homes, and large homes. Here’s how we’re defining that:
| Small Homes | Medium-sized Homes | Large Homes |
| 1-2 bedrooms | 3 bedrooms | 4+ bedrooms |
Summary of findings
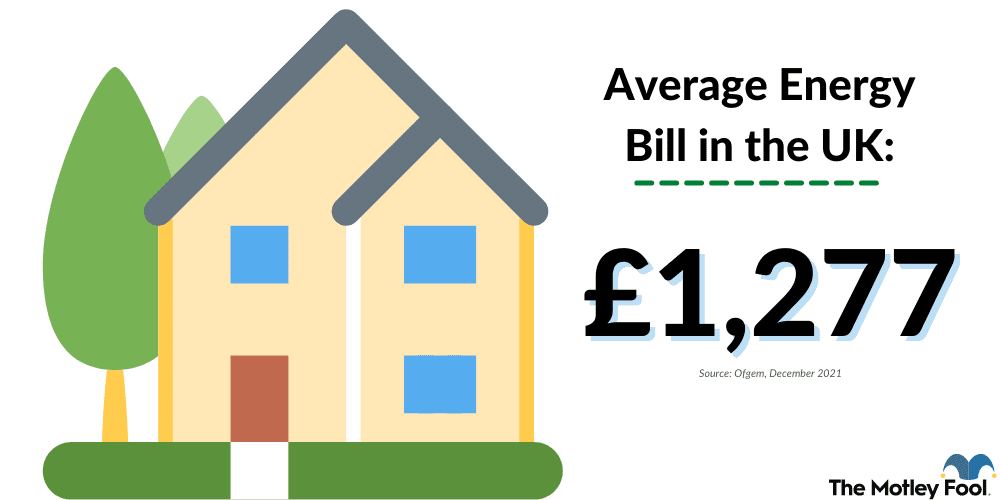
- The average energy bill in the UK stands at £1,277 as of December 2021.
- The average annual electricity bill in the UK is £294.48 for smaller homes, £474.44 for medium-sized homes, and £703.48 for larger homes.
- The average gas bill in the UK is £330.40 per year for smaller homes, £495.60 for medium-sized homes, and £702.10 for larger homes.
- The average electricity bill in the UK has increased steadily over the past decade, with UK consumers paying a combined total of £18.4billion for electricity in 2020.
- The average gas bill fell between 2010 and 2020. The combined total spend on gas during the decade fell from £14.4 billion to £12 billion according to the latest statistics.
Average UK home energy bill in the UK
The size of your energy bill depends on how large your home is. Understandably, those with the biggest homes face the highest energy bills.
The average home energy bill in the UK stands at £1,277 (as of December 2021)1.
Ofgem’s energy price cap applies to all standard variable tariffs in the UK. As a result of the cap, even though wholesale energy costs increased substantially in 2021, energy suppliers weren’t able to sell energy at capped rates and make a profit.
Average electricity bill in the UK
Those living in a small property use 1,800kWh of electricity a year. That results in an average annual cost of £294.48.
Those in a medium-sized home use an average of £2,900kWh of electricity per year. This costs an average of £474.44.
Meanwhile, those living in a large property typically use 4,300kWh of electricity per year, costing an average of £703.48.2
Average gas bill in the UK
Those living in a small house or apartment use an average of 8,000kWh of gas per year. This comes at an average annual cost of £330.40.
Meanwhile, those living in medium-sized homes typically use 12,000kWh of gas each year, which leads to an average bill of £495.60.
Those living in large properties use an average of 17,000kWh of gas each year. This results in an average gas bill of £702.10.2
Energy bills in the UK over time
The cost of electricity in the UK increased steadily during the 10 years between 2010 and 2020.
In 2010, a combined total of £13.3 billion was spent on electricity by UK consumers. By 2013, this figure had risen to £16.1 billion, before dropping to £15.3 billion a year later.
By 2018, the average combined cost of electricity in the UK had risen to £17.2 billion, increasing to £18.2 billion in 2019, and to £18.4 billion in 2020.
With regards to gas usage, Statista suggests UK household expenditure on gas was £14.4 billion back in 2010. By 2014, this had actually fallen to £14.4 billion. By 2015, the collective cost of gas in the UK increased slightly to £14.5 billion.
The price of gas was almost unchanged in 2018, with gas costing UK consumers a collective £14.1 billion. In 2019 that figure decreased slightly to £13.9 billion, before decreasing further to £12 billion by 2020.3
Updated figures are not yet available, though this figure is likely to have increased substantially in 2021 as a result of higher wholesale prices.
Factors that can influence your energy bill
Your energy bill can be influenced by a number of factors, including:
1. Your energy usage
While the current price of energy is restricted by Ofgem’s energy price cap, it only limits the unit cost of energy. In other words, the more units of energy you use, the more you will pay. As a result, your level of energy usage will have a huge impact on your energy bill.
2. The size and standard of your home
The size and standard of your home can also impact your energy bill. For example, if your home lacks cavity wall insulation, double glazing or an efficient boiler, then it’s likely that you are inadvertently wasting energy. This too will impact your energy bill.
3. The time of year
Your energy usage is likely to increase in winter. That’s because shorter days and lower temperatures mean you’ll probably have your lights and heating switched on for longer periods.
4. The appliances you use
Most electrical items have an energy efficiency rating from ‘A’ (most energy efficient) to ‘G’ (least energy efficient). The higher the rating, the less energy is needed to use the product, which can mean a lower energy bill.
5. Whether you qualify for government help
To support those on low incomes, the government offers a number of schemes to help cover energy costs:
- The Warm Home Discount: This discount pays £140 towards your energy bill between October and March. To qualify, you must either receive the ‘Guarantee Credit’ element of Pension Credit or be on a low income and meet your energy supplier’s criteria. To find out more, see our article on how you can qualify for the Warm Home Discount.
- The Cold Weather Payment: This offer runs between 1 November and 31 March every year and pays £25 for each seven-day period that the average temperature in your area hits zero degrees Celsius (or below). To qualify, you need to be on Pension Credit, Universal Credit or Income Support. Read our guide for more information on who is eligible for the Cold Weather Payment.
- The Winter Fuel Payment: For those born on or before 5 October 1954, the Winter Fuel Payment pays between £100 and £300 to help with your heating bills. You’ll get the benefit if you receive the State Pension or another social security benefit (excluding Housing Benefit, Council Tax Reduction, Child Benefit or Universal Credit). Visit the gov.uk website for more details on the Winter Fuel Payment.
Methodology
We have endeavoured to use only high-quality primary sources for this research, and have cited sources with each graph. Some of the statistics require calculations on our part and may therefore not match exactly other sources of the same information. For example, the definition of small, average, and large homes may differ across sources. Key sources include British Gas and Ofgem, the UK’s independent energy regulator.
Sources
- Infographic: Bills, prices and profits, 16 December 2021 – Ofgem
- What is the average monthly gas and electricity bill? – British Gas
- Household electricity expenditure in the United Kingdom (UK) 2010-2020, 7 December 2021 – Statista